In questo articolo potete reperire tutte le informazioni relative all’uretroplastica per la stenosi stenosi lunga dell’uretra bulbare :
- Uretroplastica bulbare in tempo unico con innesto DORSALE + VENTRALE di mucosa buccale e prepuzio
- Uretroplastica bulbare in tempo unico con innesto DORSALE + VENTRALE di mucosa buccale
- Uretroplastica bulbare 1° tempo: Perineostomia
Uretroplastica bulbare in tempo unico con innesto DORSALE + VENTRALE di mucosa buccale e prepuzio
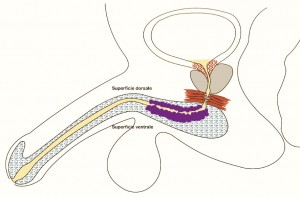
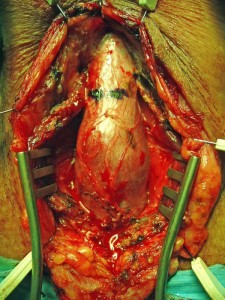
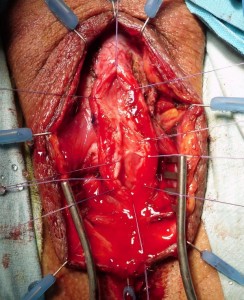
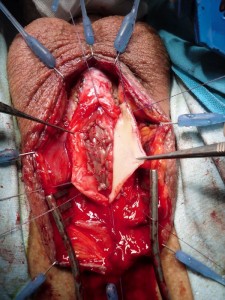
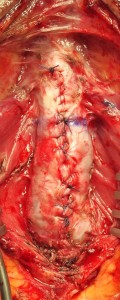
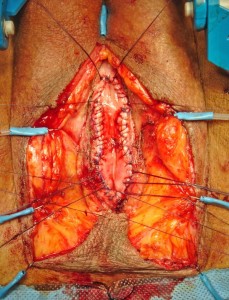
TECNICA: Incisione perineale mediana. Isolamento dell’uretra bulbare evitando, se possibile, la sezione del centro tendineo del perineo. Apertura mediana ventrale dell’uretra, lungo il tratto stenotico [foto DV1,DV15]. Incisione mediana del piatto uretrale stenotico e lateralizzazione delle due bande di spongiosa [foto DV4]. Asportazione parziale del tessuto cicatriziale uretrale a livello della stenosi. Si confeziona uretroplastica di ampliamento dorsale ed ampliamento ventrale (sec. Palminteri), con innesto dorsale di cute prepuziale (prelevata dalla faccia dorsale del pene) [foto 16 ] ed innesto ventrale di mucosa buccale [foto DV17, DV18, DV19 ]. Spongioplastica mediante sutura continua [foto DV10]. Drenaggio. Parete a strati. Si consiglia Catetere Foley 18 Fr (siliconato e scanalato) per 21 giorni (sempre collegato al sacchetto della raccolta urine).
TEMPO DI ESECUZIONE: Circa 1,5h
TERAPIA: terapia antibiotica mirata in caso di urinocoltura positiva; antibioticoprofilassi con cefalosporina di III generazione in caso di uricocoltura negativa.
GESTIONE PAZIENTE: il paziente deve rimanere a letto per 2 giorni con ghiaccio sul perineo. Ghiaccio sulla guancia dove è stato fatto il prelievo di mucosa buccale per 1 giorno. Dimissioni in 3° giornata postoperatoria.
MEDICAZIONI: La ferita perineale può essere pulita con acqua. Tra catetere e meato escono delle secrezioni-incrostazioni che vanno pulite più volte al giorno. Si consiglia di utilizzare acqua o soluzione fisiologica su una garza per pulire il catetere.
URETROCISTOGRAFIA MINZIONALE: Importante effettuare l’uretrocistografia minzionale di controllo, a 21 giorni dall’intervento chirurgico, per verificare se ci sono fistole. La percentuale di fistola uretrale insorta dopo uretroplastica bulbare, effettuate nel nostro Centro, è il 5%. Tutte le fistole uretrali sono state risolte mediante il posizionamento di catetere uretrale per ulteriori 10 o 15 o 20 giorni, a seconda dell’entità della fistola.
QUANDO IMPIEGARE QUESTO TIPO DI URETROPLASTICA:Si può fare per una stenosi bulbare corta (< 2cm) o lunga (> 2cm), ma solo se la stenosi non è obliterativa. Questo tipo di uretroplastica è utile nelle stenosi molto serrate, in cui un sono apliamento dorsale o ventrale, non sarebbe sufficiente a creare un’uretra di calibro adeguato. Se non è sufficiente un prelievo di mucosa buccale, per effettuare un ampiamento adeguato del lume uretrale, si può utilizzare un innesto dorsale di prepuzio ed un innesto ventrale di mucosa buccale. Può essere indicata nei casi di ipospadia fallita (pazienti plurioperati per ipospadia) e nella ipospadia vergine. Sconsigliata, invece, nei casi di lichen sclerosus dell’uretra e dei genitali
COMPLICANZE: sanguinamento<1%, infezione <2%. Fistola 3%
PERCENTUALE DI SUCCESSO CENTRO URETRA AREZZO: Casistica aggiornata al 30/06/2015. Effettuate 35 uretroplastiche bulbari in tempo unico con prepuzio e/o mucosa buccale. Percentuale di successo 94.6%.
CENTRO URETRA IN ITALIA: è possibile effetuare una Visita con il Dr. Palminteri o la Dr.ssa Berdondini presso una delle principali sedi: Arezzo, Torino, Milano, Modena, Roma, Napoli, Reggio Calabria, Bari, Brindisi, Palermo, Catania, Messina, Trapani.
APPROFONDIMENTI
Combined dorsal plus ventral double buccal mucosa graft in bulbar urethral reconstruction.(Palminteri E, Manzoni G, Berdondini E, Di Fiore F, Testa G, Poluzzi M, Molon A.) Eur Urol. 2008 Jan;53(1):81-9. Epub 2007 Jun 8
OBJECTIVES: We describe a technique for bulbar urethral reconstruction using a combined dorsal plus ventral double buccal mucosa graft (BMG). METHODS: From March 2002 to June 2006, 48 men, mean age 35 yr, with bulbar strictures underwent patch urethroplasty using a dorsal plus a ventral double BMG. Average stricture length was 3.65 cm (range: 2-10 cm). The stenotic urethral segment was opened along its ventral surface; the exposed dorsal urethra was incised in the midline to create an elliptical area over the tunica albuginea where the dorsal inlay BMG was placed and quilted to the corpora to augment dorsally the urethral plate. Subsequently, the ventral onlay BMG was sutured to the urethral lateral margins to complete the augmented urethroplasty. Finally, the spongiosum was closed over the graft. Successful reconstruction was defined as normal voiding without the need for any postoperative procedure including dilation. RESULTS: Mean follow-up was 22 mo (range: 13-59 mo). At the catheter removal 3 wk after surgery, in three patients the voiding cystourethrography showed a fistula, which recovered after a prolonged catheterization. Of 48 cases, 43 (89.6%) were successful and 5 (10.4%) failures with recurrence of the stricture; 4 were treated with internal urethrotomy and 1 with a temporary perineal urethrostomy.CONCLUSIONS: Preliminary results with a combined double BMG urethroplasty for severe bulbar stricture are encouraging. The double dorsal and ventral graft may provide a simple and reliable solution to achieve an adequate urethral lumen in selected patients.
Two-sided bulbar urethroplasty using dorsal plus ventral oral graft: urinary and sexual outcomes of a new technique. (Palminteri E, Berdondini E, Shokeir AA, Iannotta L, Gentile V, Sciarra A.) J Urol. 2011 May;185(5):1766-71. Epub 2011 Mar 21.
PURPOSE: Repair of bulbar strictures using anastomotic techniques may cause sexual complications, while 1-side graft urethroplasties may not be sufficient to provide an adequate lumen in narrow strictures. We evaluated the urinary and sexual results of a 2-sided dorsal plus ventral graft urethroplasty by preserving the narrow urethral plate in tight strictures. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between 2002 and 2010, 105 men with bulbar strictures underwent dorsal plus ventral graft urethroplasty. The results are reported in a homogeneous group of 73 of 105 cases in which buccal mucosa was used as a graft with findings after 1 year or more of followup. The urethra was opened ventrally, and the exposed dorsal urethra was incised in the midline to create a raw area over the tunica albuginea where the first graft was placed dorsal-inlay. Thereafter the urethra was augmented by the ventral-onlay second graft and the spongiosum was closed over itself. Successful urethral reconstruction was defined as normal voiding without the need for any postoperative procedure. Postoperative sexual dysfunction was investigated using a validated questionnaire. RESULTS: Mean followup was 48.9 months and mean stricture length was 3.3 cm. Of these 73 cases 64 (88%) were successful and 9 (12%) were treatment failures with re-stricture. Furthermore, of 49 of 73 cases who were preoperatively sexually active, none reported postoperative erectile impairment and all were satisfied with their sexual life. CONCLUSIONS: In cases of tight bulbar stricture the dorsal plus ventral buccal mucosa graft provides adequate urethral augmentation by preserving the urethral plate and avoiding postoperative sexual complications.
A systematic review of graft augmentation urethroplasty techniques for the treatment of anterior urethral strictures. (Mangera A, Patterson JM, Chapple CR.) Eur Urol. 2011 May;59(5):797-814. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Review.
CONTEXT: Reconstructive surgeons who perform urethroplasty have a variety of techniques in their armamentarium that may be used according to factors such as aetiology, stricture position, and length. No one technique is recommended. OBJECTIVE: Our aim was to assess the reported outcomes of the various techniques for graft augmentation urethroplasty according to site of surgery. EVIDENCE ACQUISITION: We performed an updated systematic review of the Medline literature from 1985 to date and classified the data according to the site of surgery and technique used. Data are also presented on the type of graft used and the follow-up methodology used by each centre. EVIDENCE SYNTHESIS: More than 2000 anterior urethroplasty procedures have been described in the literature. When considering the bulbar urethra there is no significant difference between the average success rates of the dorsal and the ventral onlay procedures, 88.4% and 88.8% at 42.2 and 34.4 mo in 934 and 563 patients, respectively. The lateral onlay technique has only been described in six patients and has a reported success rate of 83% at 77 mo. The Asopa and Palminteri techniques have been described in 89 and 53 patients with a success rate of 86.7% and 90.1% at 28.9 and 21.9 mo, respectively. When considering penile strictures, the success rate of the two-stage penile technique is significantly better than the one-stage penile technique, 90.5% versus 75.7% as calculated for 129 and 432 patients, respectively, although the follow-up of one-stage procedures was longer at 32.8 mo compared with 22.2 mo. CONCLUSIONS: There is no evidence in the literature of a difference between one-stage techniques for urethroplasty of the bulbar urethra. The two-stage technique has better reported outcomes than a one-stage approach for penile urethroplasty but has a shorter follow-up.
Uretroplastica bulbare in tempo unico con innesto DORSALE + VENTRALE di mucosa buccale
TECNICA (guarda il video B2): Incisione perineale mediana. Isolamento dell’uretra bulbare prossimale evitando, se possibile, la sezione del centro tendineo del perineo. Apertura mediana ventrale dell’uretra, lungo il tratto stenotico. Incisione mediana del piatto uretrale stenotico e lateralizzazione delle due bande di spongiosa. Asportazione parziale del tessuto cicatriziale uretrale a livello della stenosi. Si confeziona uretroplastica di ampliamento dorsale ed ampliamento ventrale sec. Palminteri, con innesto di mucosa buccale. Il prelievo di mucosa buccale può essere unico e diviso in due parti oppure, se non è sufficiente, può essere effettuato un prelievo da entrambe le guance. Spongioplastica mediante sutura continua. Drenaggio. Parete a strati. Si consiglia Catetere Foley 18 Fr (siliconato e scanalato) per 21 giorni (sempre collegato al sacchetto della raccolta urine).
TEMPO DI ESECUZIONE: Circa 1,5h
TERAPIA: Chinolonici per 5 giorni poi a seguire Monuril 1 bustina ogni 5 giorni, fino alla rimozione del catetere.
GESTIONE PAZIENTE: il paziente deve rimanere a letto per 2 giorni con ghiaccio sul perineo. Ghiaccio sulla guancia per 1 giorno. Dimissioni in 3° giornata postoperatoria.
MEDICAZIONI: La ferita perineale può essere pulita con acqua. Tra catetere e meato escono delle secrezioni-incrostazioni che vanno pulite più volte al giorno. Si consiglia di utilizzare acqua o soluzione fisiologica su una garza per pulire il catetere.
URETROCISTOGRAFIA MINZIONALE: Importante effettuare l’uretrocistografia minzionale di controllo, a 21 giorni dall’intervento chirurgico,per verificare se ci sono fistole. La percentuale di fistola uretrale insorta dopo uretroplastica bulbare, effettuate nel nostro Centro, è il 5%. Tutte le fistole uretrali sono state risolte mediante il posizionamento di catetere uretrale per ulteriori 10 o 15 o 20 giorni, a seconda dell’entità della fistola.
QUANDO IMPIEGARE QUESTO TIPO DI URETROPLASTICA:stenosi bulbare corta (< 2cm) o lunga (> 2cm), ma solo se la stenosi non è obliterativa. Questo tipo di uretroplastica è utile nelle stenosi molto serrate, in cui un sono apliamento dorsale o ventrale, non sarebbe sufficiente a creare un’uretra di calibro adeguato. Può essere indicata nei casi di lichen sclerosus dell’uretra e dei genitali, nonchè nei casi di ipospadia fallita (pazienti plurioperati per ipospadia) e nella ipospadia vergine
COMPLICANZE: sanguinamento <1%, infezione <2%. Fistola 3%
PERCENTUALE DI SUCCESSO CENTRO URETRA AREZZO: Casistica aggiornata al 30/06/2015. Effettuate 197 uretroplastiche bulbari in tempo unico con mucosa buccale. Percentuale di successo 92.4%.
CENTRO URETRA IN ITALIA: è possibile effetuare una Visita con il Dr. Palminteri o la Dr.ssa Berdondini presso una delle principali sedi: Arezzo, Torino, Milano, Modena, Roma, Napoli, Reggio Calabria, Bari, Brindisi, Palermo, Catania, Messina, Trapani.
APPROFONDIMENTI:
Combined dorsal plus ventral double buccal mucosa graft in bulbar urethral reconstruction. (Palminteri E, Manzoni G, Berdondini E, Di Fiore F, Testa G, Poluzzi M, Molon A.) Eur Urol. 2008 Jan;53(1):81-9. Epub 2007 Jun 8
OBJECTIVES: We describe a technique for bulbar urethral reconstruction using a combined dorsal plus ventral double buccal mucosa graft (BMG). METHODS: From March 2002 to June 2006, 48 men, mean age 35 yr, with bulbar strictures underwent patch urethroplasty using a dorsal plus a ventral double BMG. Average stricture length was 3.65 cm (range: 2-10 cm). The stenotic urethral segment was opened along its ventral surface; the exposed dorsal urethra was incised in the midline to create an elliptical area over the tunica albuginea where the dorsal inlay BMG was placed and quilted to the corpora to augment dorsally the urethral plate. Subsequently, the ventral onlay BMG was sutured to the urethral lateral margins to complete the augmented urethroplasty. Finally, the spongiosum was closed over the graft. Successful reconstruction was defined as normal voiding without the need for any postoperative procedure including dilation.
RESULTS: Mean follow-up was 22 mo (range: 13-59 mo). At the catheter removal 3 wk after surgery, in three patients the voiding cystourethrography showed a fistula, which recovered after a prolonged catheterization. Of 48 cases, 43 (89.6%) were successful and 5 (10.4%) failures with recurrence of the stricture; 4 were treated with internal urethrotomy and 1 with a temporary perineal urethrostomy. CONCLUSIONS: Preliminary results with a combined double BMG urethroplasty for severe bulbar stricture are encouraging. The double dorsal and ventral graft may provide a simple and reliable solution to achieve an adequate urethral lumen in selected patients.
Two-sided bulbar urethroplasty using dorsal plus ventral oral graft: urinary and sexual outcomes of a new technique. (Palminteri E, Berdondini E, Shokeir AA, Iannotta L, Gentile V, Sciarra A.) J Urol. 2011 May;185(5):1766-71. Epub 2011 Mar 21.
PURPOSE: Repair of bulbar strictures using anastomotic techniques may cause sexual complications, while 1-side graft urethroplasties may not be sufficient to provide an adequate lumen in narrow strictures. We evaluated the urinary and sexual results of a 2-sided dorsal plus ventral graft urethroplasty by preserving the narrow urethral plate in tight strictures. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between 2002 and 2010, 105 men with bulbar strictures underwent dorsal plus ventral graft urethroplasty. The results are reported in a homogeneous group of 73 of 105 cases in which buccal mucosa was used as a graft with findings after 1 year or more of followup. The urethra was opened ventrally, and the exposed dorsal urethra was incised in the midline to create a raw area over the tunica albuginea where the first graft was placed dorsal-inlay. Thereafter the urethra was augmented by the ventral-onlay second graft and the spongiosum was closed over itself. Successful urethral reconstruction was defined as normal voiding without the need for any postoperative procedure. Postoperative sexual dysfunction was investigated using a validated questionnaire. RESULTS: Mean followup was 48.9 months and mean stricture length was 3.3 cm. Of these 73 cases 64 (88%) were successful and 9 (12%) were treatment failures with re-stricture. Furthermore, of 49 of 73 cases who were preoperatively sexually active, none reported postoperative erectile impairment and all were satisfied with their sexual life. CONCLUSIONS: In cases of tight bulbar stricture the dorsal plus ventral buccal mucosa graft provides adequate urethral augmentation by preserving the urethral plate and avoiding postoperative sexual complications.
A systematic review of graft augmentation urethroplasty techniques for the treatment of anterior urethral strictures. (Mangera A, Patterson JM, Chapple CR.) Eur Urol. 2011 May;59(5):797-814. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Review.
CONTEXT: Reconstructive surgeons who perform urethroplasty have a variety of techniques in their armamentarium that may be used according to factors such as aetiology, stricture position, and length. No one technique is recommended. OBJECTIVE: Our aim was to assess the reported outcomes of the various techniques for graft augmentation urethroplasty according to site of surgery. EVIDENCE ACQUISITION: We performed an updated systematic review of the Medline literature from 1985 to date and classified the data according to the site of surgery and technique used. Data are also presented on the type of graft used and the follow-up methodology used by each centre. EVIDENCE SYNTHESIS: More than 2000 anterior urethroplasty procedures have been described in the literature. When considering the bulbar urethra there is no significant difference between the average success rates of the dorsal and the ventral onlay procedures, 88.4% and 88.8% at 42.2 and 34.4 mo in 934 and 563 patients, respectively. The lateral onlay technique has only been described in six patients and has a reported success rate of 83% at 77 mo. The Asopa and Palminteri techniques have been described in 89 and 53 patients with a success rate of 86.7% and 90.1% at 28.9 and 21.9 mo, respectively. When considering penile strictures, the success rate of the two-stage penile technique is significantly better than the one-stage penile technique, 90.5% versus 75.7% as calculated for 129 and 432 patients, respectively, although the follow-up of one-stage procedures was longer at 32.8 mo compared with 22.2 mo. CONCLUSIONS: There is no evidence in the literature of a difference between one-stage techniques for urethroplasty of the bulbar urethra. The two-stage technique has better reported outcomes than a one-stage approach for penile urethroplasty but has a shorter follow-up.
Uretroplastica bulbare 1° tempo: Perineostomia
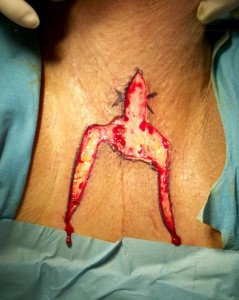
TECNICA: Incisione perineale ad U rovesciata [foto PER1]. Isolamento dell’uretra bulbare medio-prossimale evitando la sezione del centro tendineo del perineo [foto PER2]. Apertura mediana ventrale dell’uretra, lungo il tratto stenotico e sutura dei margini della spongiosa [foto PER3]. Creazione della perineostomia [foto PER4, PER5]. Catetere Foley 18 Fr (siliconato e scanalato) per 7-10 giorni non necessariamente collegato al sacchetto della raccolta urine. Medicazione con garze di connettivina legate chirurgicamente [foto PER6]
TEMPO DI ESECUZIONE: Circa 1,5h
TERAPIA: terapia antibiotica mirata in caso di urinocoltura positiva; antibioticoprofilassi con cefalosporina di III generazione in caso di uricocoltura negativa.
GESTIONE PAZIENTE: il paziente deve rimanere a letto per 3 giorni con ghiaccio sul perineo. Dimissioni in 4° giornata postoperatoria.
MEDICAZIONI: Rimuovere le garze legate chirurgicamente in 3° giornata postoperatoria. Disinfezione della ferita con Betadine soluzione e Garze di connettivina per 20 giorni.
QUANDO IMPIEGARE QUESTO TIPO DI URETROPLASTICA:quando l’uretra peno-bulbare è molto danneggiata e non fruibile per una chirurgia in tempo unico. Può essere indicata nei casi di lichen sclerosus dell’uretra e dei genitali, nonchè nei casi di ipospadia fallita (pazienti plurioperati per ipospadia) e nella ipospadia vergine
COMPLICANZE: sanguinamento<3%, infezione <5%.
PERCENTUALE DI SUCCESSO CENTRO URETRA AREZZO: Casistica aggiornata al 30/06/2015. Effettuate 297 perineostomie. Percentuale di successo 80.1%.
CENTRO URETRA IN ITALIA: èpossibile effetuare una Visita con il Dr. Palminteri o la Dr.ssa Berdondini presso una delle principali sedi: Arezzo, Torino, Milano, Modena, Roma, Napoli, Reggio Calabria, Bari, Brindisi, Palermo, Catania, Messina, Trapani.
APPROFONDIMENTI:
Urethroplasty by scrotal flap for long urethral strictures Blandy JP, et Al. Br J Urol 1968; 40: 261 * No abstract availableNew 2-stage buccal mucosal graft urethroplasty. Palminteri E, et Al.J Urol. 2002 Jan;167(1):130-2.
PURPOSE: Previously buccal mucosal grafts used for repairing adult bulbourethral stricture with the 1-stage dorsal technique has provided a satisfactory outcome in our experience. We present the wider use of buccal mucosal grafts for 2-stage urethroplasty. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A total of 24 men 25 to 60 years old (median age 45) with a complex bulbar stricture underwent 2-stage urethroplasty using a buccal mucosal graft to repair the perineostomy. The primary etiology of stricture was traumatic in 4 cases, inflammatory in 16 and unknown in 4. The 2 x 6 cm. graft was harvested from the inner cheek and sutured to the left margin of the urethral mucosal plate with running 6-zero polyglactin suture. Patients were discharged from the hospital within 3 days with a 14Fr silicone urethral catheter in place. Radiological studies and urethroscopy were done 1 year after closure. RESULTS: A final successful outcome with no recurrent stricture was achieved in 23 of 24 men (92.8%) at a median followup of 18 months (range 13 to 32). In 1 case a urethrocutaneous fistula at the initial radiological assessment closed spontaneously after 14 days of catheterization. No urethral diverticula developed. The mean postoperative peak flow rate is 22 ml. per second (range 18 to 25). CONCLUSIONS: Our new 2-stage buccal mucosal graft urethroplasty may be an excellent technique for complex bulbar urethral stricture disease. Our suggestions may increase usefulness of the 2-stage technique for repairing complex strictures due to the avoidance of classic complications.